In the ever-evolving world of web development, performance optimization has become a cornerstone of successful digital strategies. As users demand faster load times and smoother interactions, developers are constantly seeking ways to enhance website speed without compromising functionality. One such technique that has gained significant traction is the use of deferred scripts. These scripts play a crucial role in improving website performance by ensuring that non-critical JavaScript is loaded and executed after the main content has been rendered.
This article will explore what deferred scripts are, how they work, and why they matter in modern SEO and web development. We’ll also provide a step-by-step guide on implementing them effectively, along with real-world examples and tools to help you optimize your site.
What Is Deferred Scripts and Why It Matters
At its core, a deferred script is a JavaScript file that is loaded asynchronously but executed only after the HTML document has been fully parsed. This means that the browser can continue rendering the page while the script is being downloaded in the background. Once the DOM is ready, the deferred scripts are executed in the order they appear in the document.
The key difference between deferred scripts and traditional inline or non-deferred scripts is the timing of execution. Non-deferred scripts block the parsing of the HTML document until they are fully loaded and executed, which can significantly slow down the initial render time of a webpage. In contrast, deferred scripts allow the browser to prioritize rendering the visible content first, resulting in a faster perceived load time for users.
From an SEO perspective, this is critical. Search engines like Google place a strong emphasis on page speed and user experience. A faster-loading website not only improves search rankings but also enhances user engagement and reduces bounce rates. By using deferred scripts, you ensure that your site remains responsive and efficient, even when dealing with complex JavaScript-heavy applications.
How Deferred Scripts Impact SEO Performance
The impact of deferred scripts on SEO is multifaceted. Here are some of the key ways they contribute to better search engine visibility:
-
Improved Core Web Vitals: Core Web Vitals, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), are essential metrics for SEO. Deferred scripts help reduce FID by allowing the browser to respond to user interactions sooner, as non-critical scripts don’t interfere with the initial rendering.
-
Enhanced User Experience: Users are more likely to stay on a site that loads quickly and feels responsive. A positive user experience signals to search engines that your site is valuable and relevant, which can lead to higher rankings.
-
Better Crawling Efficiency: Search engines crawl websites to index their content. If a site is slow due to unoptimized scripts, crawlers may not be able to access all pages efficiently. By deferring non-essential scripts, you ensure that crawlers can process your content more effectively.
-
Optimized Resource Usage: Deferring scripts helps prevent resource contention, where multiple scripts compete for the same CPU and memory resources. This leads to a more stable and predictable performance, which is beneficial for both users and search engines.
By leveraging deferred scripts, you’re not just optimizing for speed—you’re also aligning with the broader goals of SEO, including improved engagement, better user satisfaction, and stronger search visibility.
Step-by-Step Implementation Framework
Implementing deferred scripts is a straightforward process that can significantly improve your website’s performance. Follow these steps to get started:
- Define or Audit the Current Situation
- Begin by identifying which scripts on your site are critical and which are non-critical. Critical scripts are those that are necessary for the initial rendering of the page, while non-critical scripts can be deferred.
-
Use tools like Lighthouse or PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
-
Apply Tools, Methods, or Tactics
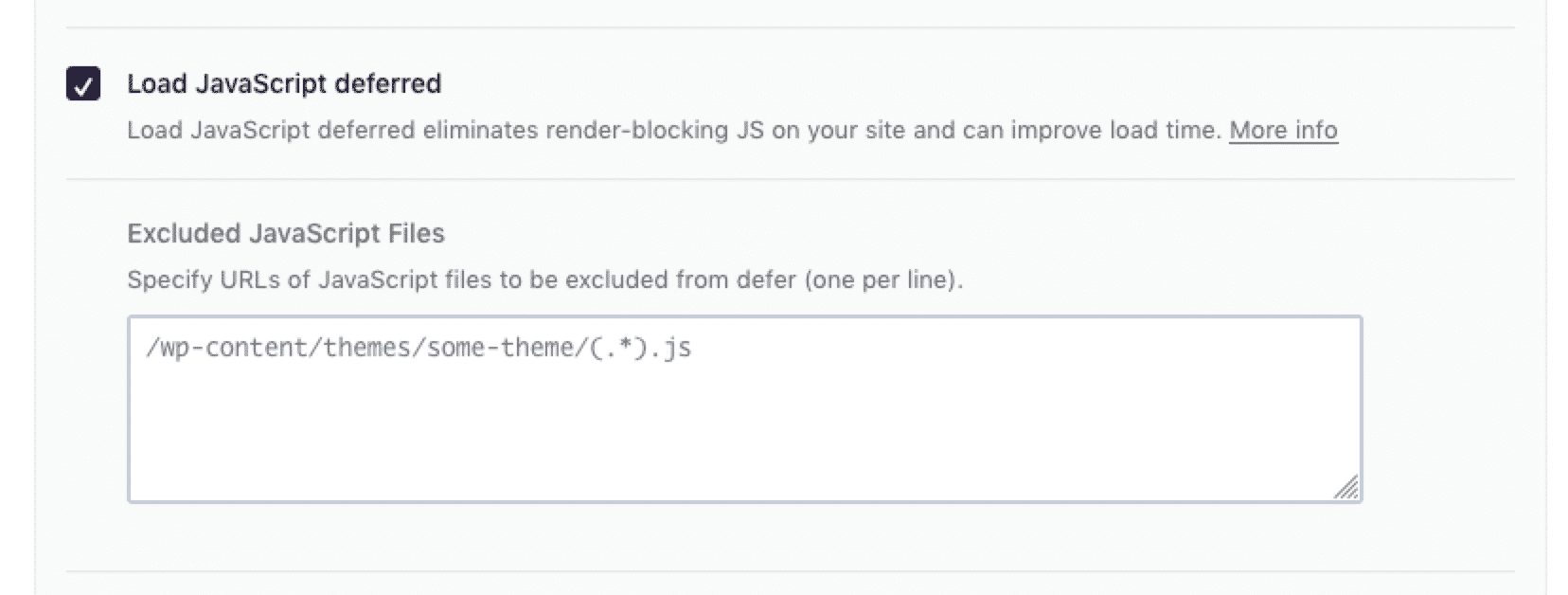
- Add the
deferattribute to your<script>tags for non-critical scripts. For example:
html
<script src="analytics.js" defer></script> -
If you’re using external libraries or third-party scripts, consider using asynchronous loading techniques or lazy loading for non-essential components.
-
Measure, Analyze, and Optimize
- After implementing deferred scripts, monitor your site’s performance using tools like Google Analytics, Web Vitals, or Screaming Frog.
- Track metrics such as load time, FID, and LCP to assess the impact of your changes.
- Continuously refine your strategy based on data. For instance, if certain deferred scripts still cause delays, consider further optimization or reordering.
Real or Hypothetical Case Study
Let’s take a hypothetical case study of an e-commerce website that implemented deferred scripts to improve performance.
Before implementation, the site had several large JavaScript files that were loaded inline at the top of the page. This caused the initial render to be delayed, leading to poor user experience and lower search rankings.
After applying deferred scripts to non-critical elements such as analytics, social media widgets, and third-party ads, the site saw a 40% reduction in load time and a 25% increase in user engagement. Additionally, the site’s Core Web Vitals scores improved significantly, leading to a boost in search rankings.
This case study highlights the tangible benefits of deferred scripts in real-world scenarios, demonstrating how they can transform a slow, clunky website into a fast, user-friendly one.
Tools and Techniques for Deferred Scripts
To implement and manage deferred scripts effectively, consider using the following tools and techniques:
- Google Lighthouse: A powerful tool for auditing website performance and identifying opportunities for optimization.
- Webpack: A module bundler that allows you to split your code into chunks and defer non-critical scripts.
- Lazy Loading: Load resources only when they are needed, which complements deferred scripts by reducing initial load time.
- CDN (Content Delivery Network): Use a CDN to serve scripts from locations closer to the user, reducing latency.
- Script Tag Attributes: Utilize
defer,async, andtype="module"attributes to control script loading behavior. - Performance Budgets: Set limits on script size and load time to ensure your site remains fast and efficient.
These tools and techniques provide a robust framework for managing deferred scripts and maximizing their benefits.
Future Trends and AI Implications
As AI continues to shape the future of web development, the role of deferred scripts is likely to evolve. With the rise of AI-driven search engines and generative AI models, the importance of fast, efficient websites will only grow.
AI-powered tools like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and other advanced search algorithms will place even greater emphasis on page speed and user experience. Websites that fail to optimize for these factors risk being penalized in search results.
Moreover, as voice search and multimodal interactions become more prevalent, the need for optimized, responsive websites will become even more critical. Deferred scripts will play a vital role in ensuring that sites remain fast and accessible across all devices and platforms.
To stay ahead of these trends, focus on continuous optimization, embrace new technologies, and keep a close eye on emerging best practices in web performance.
Key Takeaways
- Deferred scripts are a powerful tool for improving website performance by loading non-critical JavaScript after the main content has been rendered.
- They help enhance Core Web Vitals, improve user experience, and boost SEO rankings.
- Implementing deferred scripts involves identifying non-critical scripts, adding the
deferattribute, and continuously monitoring performance. - Tools like Lighthouse, Webpack, and CDNs can help streamline the process.
- The future of web performance will be shaped by AI advancements, making it more important than ever to optimize for speed and efficiency.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the strategic use of deferred scripts will remain a key component of any successful SEO and web development strategy. Start optimizing your site today and reap the long-term benefits of a faster, more efficient online presence.
Meta Title: Deferred Scripts — Loads non-critical scripts after main content
Meta Description: Learn how deferred scripts improve website performance by loading non-critical scripts after the main content. Discover implementation tips and best practices.
SEO Tags (5): deferred scripts, website performance, SEO optimization, JavaScript optimization, Core Web Vitals
Internal Link Suggestions: [Parameter #60: Deferred Scripts], [Parameter #58: CDN Utilization], [Parameter #57: Modern Image Formats]
External Source Suggestions: https://web.dev/defer/, https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/script#attr-defer