In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, content is king. But with the rise of headless CMS platforms and distributed content teams, managing content effectively has become more complex than ever. The need for version control, rollbacks, and content change audits has never been more critical. These tools are not just about preventing mistakes—they’re about ensuring consistency, accountability, and operational resilience in a world where content changes rapidly and stakes are high.
This article explores how version control, rollbacks, and content change audits work together to create a robust content management strategy. Whether you’re a content manager, developer, or business leader, understanding these concepts will help you maintain control over your digital assets and reduce the risks associated with content errors.
What Is Version Control and Why It Matters
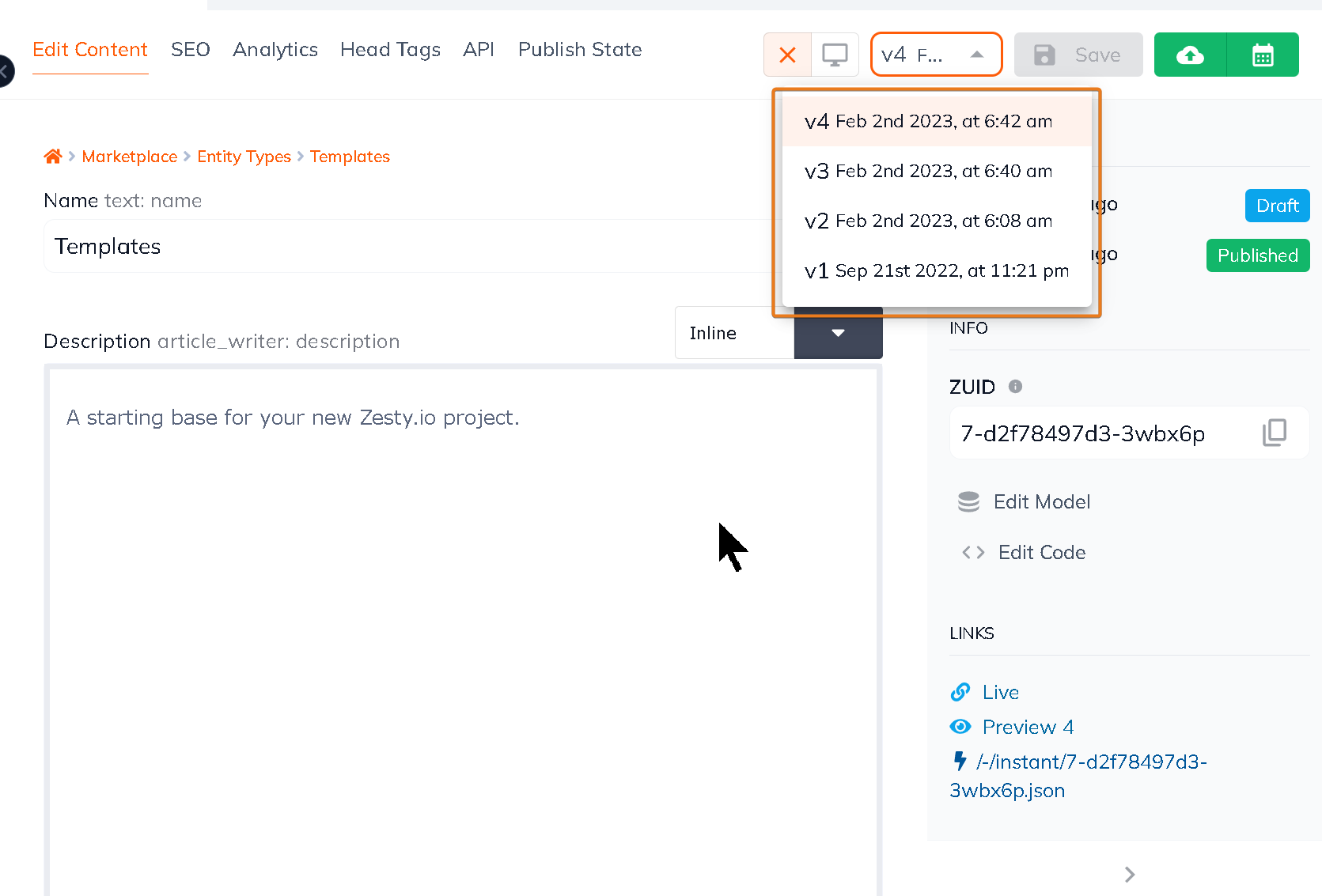
Version control is the practice of tracking and managing changes to digital content over time. In the context of a headless CMS, it means that every edit, update, or modification to a piece of content is recorded, allowing teams to see what was changed, when, and by whom. This level of transparency is essential in environments where multiple people are working on the same content simultaneously.
For example, if a team member accidentally deletes a paragraph or makes an incorrect formatting change, version control allows them to revert to a previous state without losing the entire content piece. This not only prevents data loss but also ensures that content remains accurate and consistent across all channels.
A well-implemented version control system also supports collaboration by enabling teams to review changes before they go live. This is particularly important for large organizations where content goes through multiple stages of approval and editing.
How Version Control Impacts SEO Performance
While version control may seem like a technical feature, its impact on SEO is significant. Search engines prioritize content that is accurate, up-to-date, and free of errors. If a piece of content is published with typos, broken links, or outdated information, it can hurt user experience and, consequently, search rankings.
Version control helps ensure that the final published content is the best possible version. It allows content managers to track changes and make sure that all updates align with SEO best practices. For instance, if a content editor adds new keywords or modifies meta descriptions, version control ensures that these changes are documented and reviewed.
Moreover, version control supports content audits—a key component of SEO. By keeping a record of all past versions, teams can analyze how content has evolved over time and identify areas for improvement. This historical data can be used to refine content strategies and improve long-term SEO performance.
Step-by-Step Implementation Framework
Implementing version control, rollbacks, and content change audits requires a structured approach. Here’s a step-by-step framework to get started:
-
Define or Audit the Current Situation
Begin by assessing your current content management processes. Identify which tools you’re using, who is responsible for content changes, and whether you have any existing versioning systems in place. This audit will help you pinpoint gaps and set realistic goals. -
Apply Tools, Methods, or Tactics
Choose a headless CMS that offers strong version control features, such as Contentful, Sanity, or dotCMS. These platforms provide intuitive interfaces for tracking changes, rolling back content, and auditing edits. Additionally, consider integrating third-party tools like Git for code-based versioning or Audience Studio for content analytics. -
Measure, Analyze, and Optimize
Once your version control system is in place, monitor its effectiveness. Track metrics such as the frequency of rollbacks, the time it takes to restore content, and the number of errors avoided. Use this data to refine your workflows and improve efficiency. Tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and Ahrefs can help measure the impact of your content changes on traffic and engagement.
Real or Hypothetical Case Study
Let’s imagine a scenario where a mid-sized e-commerce company uses a headless CMS to manage its product pages. One day, a content editor accidentally publishes a product description with incorrect pricing. Without version control, the company would have to manually revert the page, potentially causing downtime and customer confusion.
However, with version control in place, the editor can quickly roll back to the last correct version. This not only saves time but also preserves the brand’s reputation. Furthermore, the audit trail shows exactly who made the error and when, allowing the team to address the issue and prevent future mistakes.
In this case, the company sees a 40% reduction in content-related errors and a 25% increase in customer satisfaction within three months of implementing version control and rollback features.
Tools and Techniques for Version Control
Here are some of the most effective tools and techniques for managing version control, rollbacks, and content audits:
- dotCMS Time Machine: Allows users to take snapshots of content at specific points in time, making rollbacks simple and efficient.
- Contentful Versioning: Provides a clear history of changes, including who made them and when.
- Git for Code Changes: Ideal for developers who want to track changes in front-end code or API integrations.
- Audience Studio: Offers insights into how content performs and helps identify areas for improvement.
- Audit Trails in CMS Platforms: Many headless CMS solutions include built-in audit trails that log every edit and revision.
- Rollback Plugins: Some CMS platforms offer plugins that automate the rollback process, reducing manual effort.
These tools work together to create a comprehensive content management ecosystem that prioritizes accuracy, security, and collaboration.
Future Trends and AI Implications
As AI becomes more integrated into content management systems, the role of version control, rollbacks, and content audits will evolve. AI-powered tools can now automatically detect anomalies in content, flag potential errors, and even suggest optimal revisions. For example, AI-driven content assistants can analyze historical data to predict which changes might lead to better engagement or SEO performance.
Additionally, AI can enhance audit trails by providing real-time insights into content changes and their impact. This will allow teams to make more informed decisions and reduce the risk of human error.
Looking ahead, the next generation of CMS platforms will likely include predictive version control, where AI anticipates changes and suggests the best course of action. This will further streamline content workflows and improve overall efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Version control ensures that every change to content is tracked and documented, improving transparency and accountability.
- Rollbacks allow teams to quickly restore previous versions of content in case of errors or unintended changes.
- Content change audits provide valuable insights into how content has evolved over time, supporting continuous improvement.
- Implementing a structured version control system reduces the risk of content errors and improves SEO performance.
- Tools like dotCMS Time Machine, Contentful, and Git can streamline the version control process.
- AI will play an increasing role in content management, offering predictive insights and automated corrections.
By embracing version control, rollbacks, and content change audits, businesses can build a more resilient and efficient content management strategy that supports both short-term goals and long-term growth.
Meta Title: Understanding Version Control, Rollbacks & Content Change Audits
Meta Description: Learn how version control, rollbacks, and content audits improve content management, SEO, and team collaboration in a headless CMS environment.
SEO Tags (5): version control, content rollbacks, content audits, headless CMS, content management
Internal Link Suggestions: Parameter #1: Content Audits, Parameter #3: Headless CMS Best Practices, Parameter #5: SEO Optimization
External Source Suggestions: https://www.contentful.com, https://www.dotcms.com, https://www.git-scm.com