In the ever-evolving world of web development, speed is no longer just a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity. With Google’s Core Web Vitals now a critical ranking factor and users expecting near-instant load times, optimizing your WordPress site’s CSS and JavaScript delivery has never been more important. Whether you’re managing a small blog or a high-traffic e-commerce platform, ensuring that your CSS and JS files are delivered efficiently can significantly improve user experience, SEO performance, and conversion rates.
This article will guide you through the essential steps to optimize CSS and JS delivery on your WordPress site, helping you achieve faster load times, better rankings, and a smoother browsing experience for your visitors.
What Is CSS & JS Optimization and Why It Matters
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) and JavaScript (JS) are two of the most critical resources on any website. They control how your site looks and functions, but they can also be major contributors to slow load times if not properly optimized.
CSS optimization involves reducing the size of your style sheets by removing unnecessary code, such as comments, white space, and unused styles. This helps the browser render your page faster.
JavaScript optimization focuses on minimizing the size of your scripts, deferring non-critical JS, and ensuring that scripts don’t block the rendering of your page. Optimizing JS can drastically reduce the time it takes for your site to become interactive.
Together, these optimizations help reduce file sizes, minimize HTTP requests, and improve the overall performance of your WordPress site.
Why does this matter? According to Google, a one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% drop in conversions. Additionally, PageSpeed Insights and other tools often flag unoptimized CSS and JS as key areas for improvement. By addressing these issues, you not only improve your site’s speed but also boost your SEO and user engagement.
How CSS & JS Optimization Impacts SEO Performance
Optimizing CSS and JS directly affects several core aspects of SEO:
1. Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—are now major ranking factors. Optimized CSS and JS help improve these metrics by:
- Reducing LCP by ensuring styles and scripts are loaded efficiently.
- Minimizing FID by preventing JS from blocking the main thread.
- Improving CLS by avoiding layout shifts caused by unoptimized assets.
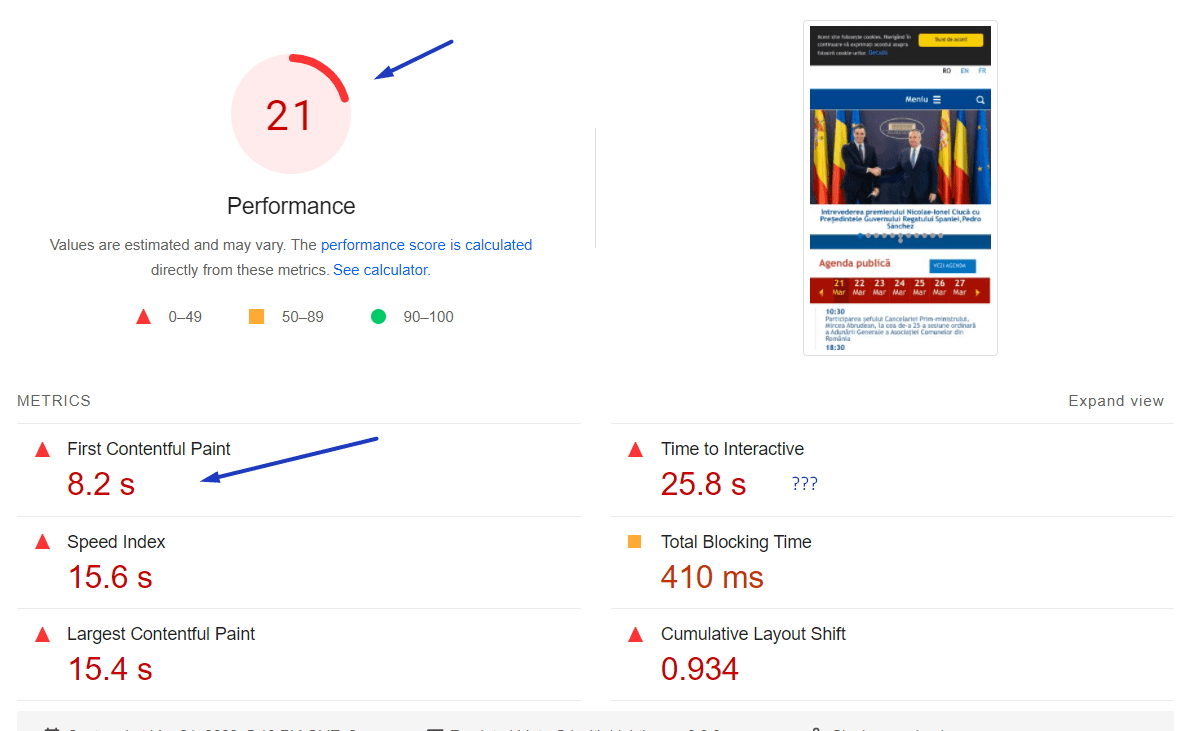
2. PageSpeed Insights Score
Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool provides actionable recommendations for improving your site’s performance. If your CSS or JS isn’t minified or deferred, your score will suffer. Optimizing these files can lead to significant improvements in your score and better visibility in search results.
3. User Experience and Bounce Rates
A fast-loading site keeps users engaged. Studies show that users are more likely to abandon a site if it takes more than three seconds to load. Optimizing CSS and JS ensures your site loads quickly, keeping users on your pages and reducing bounce rates.
Step-by-Step Implementation Framework
Here’s a practical, step-by-step approach to optimizing CSS and JS delivery on your WordPress site.
1. Audit Your Current Setup
Before making any changes, understand what you’re working with. Use tools like:
- Google PageSpeed Insights – To identify issues with CSS and JS.
- GTmetrix – For detailed performance reports and suggestions.
- WebPageTest – To simulate real-world load times across different locations.
These tools will give you insights into which files are causing delays and where you can make improvements.
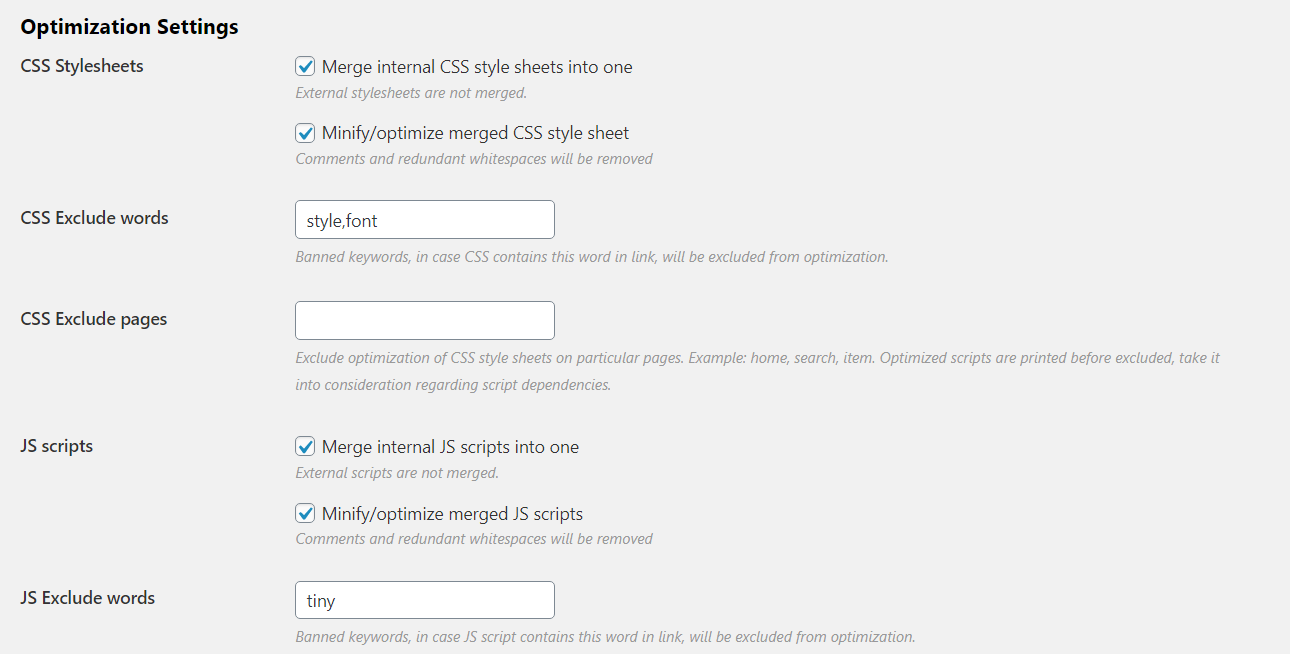
2. Minify CSS and JavaScript
Minification removes unnecessary characters (like spaces, line breaks, and comments) from your code, resulting in smaller file sizes.
How to do it:
- Use a Plugin: Plugins like WP Rocket, Autoptimize, and Asset CleanUp automatically minify your CSS and JS files.
- Manual Minification: You can use online tools like CleanCSS.com or UglifyJS to minify your code manually.
- Server-Side Minification: Some hosting providers offer built-in minification options, or you can configure it via
.htaccessor server modules.
3. Defer Non-Essential JavaScript
Deferring JavaScript means loading it after the initial content has been rendered. This prevents JS from blocking the rendering of your page.
How to do it:
- Use the
deferAttribute: Adddeferto your<script>tags so the browser loads the script after parsing the HTML. - Use a Plugin: Plugins like WP Rocket and Autoptimize can automatically defer non-critical JS.
4. Combine CSS and JS Files
Combining multiple CSS or JS files into one reduces the number of HTTP requests, which improves load times.
Best Practices:
- Combine only related files to avoid bloating your site.
- Ensure compatibility after combining files, especially if you’re using third-party plugins.
5. Enable GZIP Compression
GZIP compression reduces the size of your CSS and JS files even further, making them faster to download.
How to enable GZIP:
- Using a Plugin: Most caching plugins (like WP Rocket) automatically enable GZIP.
- Manually via .htaccess: Add the following code to your
.htaccessfile:
apache
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/rss+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript
</IfModule>
6. Leverage Browser Caching
Browser caching stores static files locally, so returning visitors don’t have to re-download them.
How to set it up:
- Use a caching plugin like WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache.
- Configure cache expiration times in your
.htaccessfile or via your hosting provider.
7. Monitor and Test
After implementing optimizations, use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and Pingdom to monitor your site’s performance.
Check for any issues, such as broken layouts or functionality, and adjust your settings accordingly.
Real or Hypothetical Case Study
Let’s take a look at a hypothetical scenario where a WordPress site improved its performance through CSS and JS optimization.
Scenario: A mid-sized e-commerce site had an average load time of 6.5 seconds, leading to high bounce rates and poor SEO performance.
Actions Taken:
- Enabled WP Rocket to minify and compress CSS and JS.
- Deferred non-critical JavaScript.
- Combined and optimized CSS and JS files.
- Enabled GZIP compression.
Results:
- Load time dropped to 2.8 seconds.
- PageSpeed Insights score increased from 62 to 92.
- Bounce rate decreased by 30%.
- Conversion rate improved by 15%.
This case study shows how effective CSS and JS optimization can be when implemented correctly.
Tools and Techniques for CSS & JS Optimization
Here are some of the best tools to help you optimize your WordPress site’s CSS and JS delivery:
- WP Rocket – A powerful all-in-one plugin that handles minification, compression, caching, and more.
- Autoptimize – Free plugin that optimizes CSS, JS, and HTML.
- Asset CleanUp – Helps remove unused CSS and JS from your site.
- Cloudflare – Offers automatic minification and caching for your assets.
- GTmetrix – Provides detailed performance reports and optimization suggestions.
- PageSpeed Insights – Google’s tool for analyzing and improving your site’s speed.
Future Trends and AI Implications
As AI continues to shape the future of web development, we can expect even more advanced tools for optimizing CSS and JS delivery.
AI-driven performance tools may soon be able to:
- Automatically detect and remove unused CSS/JS.
- Predict the best way to combine and compress files based on user behavior.
- Provide real-time recommendations for optimization.
WordPress itself is also evolving, with more built-in features for performance optimization. As AI becomes more integrated into CMS platforms, developers will have even more powerful tools at their disposal.
For now, the best approach is to stay proactive, keep your site updated, and leverage the latest optimization techniques.
Key Takeaways
- Minify CSS and JS to reduce file sizes and improve load times.
- Defer non-essential JavaScript to prevent render-blocking.
- Combine CSS and JS files to reduce HTTP requests.
- Enable GZIP compression for faster delivery of assets.
- Leverage browser caching to improve performance for returning visitors.
- Use tools like WP Rocket, Autoptimize, and Cloudflare to automate optimization.
- Regularly monitor your site’s performance with tools like GTmetrix and PageSpeed Insights.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll not only improve your site’s speed but also enhance user experience, boost SEO rankings, and increase conversions.
Meta Title: How to Optimize CSS & JS Delivery on WordPress for Faster Load Times
Meta Description: Learn how to optimize CSS and JS delivery on your WordPress site for faster load times, improved SEO, and better user experience.
SEO Tags (5): WordPress optimization, CSS optimization, JS optimization, site speed, WordPress performance
Internal Link Suggestions:
– [Parameter #1: WordPress Caching Strategies]
– [Parameter #2: Image Optimization for WordPress]
– [Parameter #3: Core Web Vitals for SEO]
External Source Suggestions:
– https://pagespeed.web.dev
– https://gtmetrix.com
– https://wordpress.org/plugins/wp-rocket/