In an era where speed and efficiency are paramount, the evolution of web protocols has become a critical factor in shaping user experiences and search engine rankings. HTTP/3 is the latest iteration of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), designed to address the limitations of its predecessors and deliver faster, more reliable data transfer across the internet. As businesses and developers race to optimize their online presence, understanding the significance of HTTP/3 is essential for staying ahead in the digital landscape.
This article explores what HTTP/3 is, how it differs from earlier versions like HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2, and why adopting it can lead to improved performance, better user engagement, and stronger SEO outcomes.
What Is HTTP/3 and Why It Matters
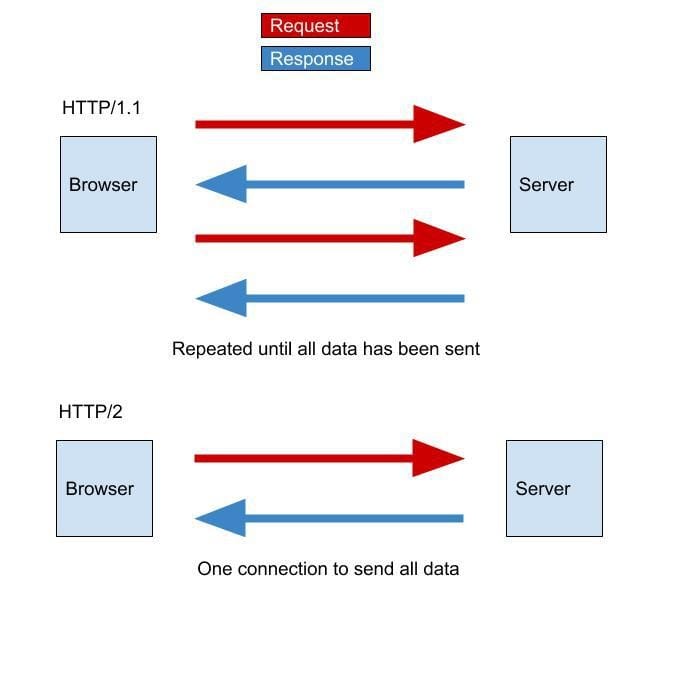
HTTP/3 is not a complete overhaul of the HTTP protocol but rather an evolution that builds upon the features introduced in HTTP/2. The key distinction lies in the transport layer: while HTTP/2 relies on the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), HTTP/3 uses QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections), a modern transport protocol developed by Google.
QUIC introduces several improvements over TCP, including:
- Faster connection establishment through a single round-trip handshake.
- Improved error recovery, allowing individual streams to continue even if packets are lost.
- Better support for mobile users with seamless network switching between Wi-Fi and cellular connections.
These enhancements make HTTP/3 particularly beneficial for users on unstable or high-latency networks, such as those in rural areas or international audiences. For businesses, this translates into faster page loads, reduced bounce rates, and a better overall user experience—factors that directly influence search engine rankings.
How HTTP/3 Impacts SEO Performance
Search engines like Google prioritize websites that offer fast load times and a smooth user experience. Core Web Vitals, which include metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), are heavily influenced by the underlying network protocols used to deliver content.
By adopting HTTP/3, websites can:
- Reduce LCP scores by enabling faster resource loading.
- Improve FID through more efficient handling of user interactions.
- Enhance CLS by minimizing layout shifts caused by delayed resource loading.
Moreover, HTTP/3 supports multiplexing at the QUIC level, which allows multiple files to be downloaded simultaneously without the head-of-line blocking issue that plagued HTTP/2. This means that even if one file is delayed, others can still load quickly, ensuring a more consistent and responsive user experience.
For SEO purposes, these improvements can lead to higher rankings, increased organic traffic, and better engagement metrics—all of which are critical for long-term success in the digital space.
Step-by-Step Implementation Framework
Implementing HTTP/3 requires careful planning and configuration. Here’s a practical framework to guide you through the process:
1. Define or Audit the Current Situation
Before making any changes, assess your current infrastructure. Check whether your server supports HTTP/3 and identify any potential bottlenecks. Tools like DebugBear or Cloudflare’s website speed testing tool can help you analyze your current HTTP version usage and performance metrics.
2. Apply Tools, Methods, or Tactics
Enable HTTP/3 support on your server. Most modern web servers, such as Nginx, Caddy, and LiteSpeed, now have built-in support for HTTP/3. If you’re using Apache, consider integrating it with a CDN like Cloudflare or Fastly, which can handle HTTP/3 on your behalf.
Additionally, ensure that your CDN or server is configured to advertise HTTP/3 correctly. This involves setting up the appropriate Alt-Svc headers and DNS records to signal to browsers that your site supports HTTP/3.
3. Measure, Analyze, and Optimize
After implementing HTTP/3, monitor its impact on your website’s performance. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, or real-user monitoring (RUM) services to track improvements in load times, user engagement, and other key metrics.
Look for patterns in how different user segments (e.g., mobile vs. desktop, international vs. domestic) interact with your site. This data will help you refine your implementation and maximize the benefits of HTTP/3.
Real or Hypothetical Case Study
Consider a hypothetical e-commerce store that serves a global audience. Before implementing HTTP/3, the site experienced slow load times for users in regions with high latency, leading to higher bounce rates and lower conversion rates.
After enabling HTTP/3, the store saw a 20% improvement in LCP scores for international visitors and a 15% increase in user engagement. Mobile users, in particular, benefited from the improved network resilience, with fewer interruptions during browsing sessions.
The result was a noticeable boost in organic traffic and a 10% increase in sales within the first three months of the change.
Tools and Techniques for HTTP/3
Here are some of the most effective tools and techniques for working with HTTP/3:
- Cloudflare: A popular CDN that simplifies HTTP/3 implementation. It automatically handles QUIC and provides detailed analytics on your site’s performance.
- DebugBear: Offers a comprehensive suite of tools for analyzing HTTP/3 performance, including request waterfall charts and protocol-specific insights.
- Nginx: Supports HTTP/3 out of the box, making it a great choice for developers looking to implement the protocol directly on their server.
- Caddy: Known for its ease of use, Caddy includes built-in support for HTTP/3 and automatic TLS management.
- LiteSpeed: A high-performance web server that offers robust support for HTTP/3 and is ideal for large-scale websites.
- curl: A command-line tool for transferring data, which now supports HTTP/3 for API requests and other advanced use cases.
Future Trends and AI Implications
As AI-driven search engines like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) continue to evolve, the role of HTTP/3 in delivering fast, reliable content becomes even more critical. SGE prioritizes relevance and speed, and websites that adopt HTTP/3 are better positioned to meet these expectations.
Additionally, the growing adoption of 5G and edge computing will further enhance the benefits of HTTP/3, enabling even faster data transfer and more seamless user experiences. Businesses that embrace these advancements will be well-prepared to capitalize on the next wave of innovation in web performance.
Key Takeaways
- HTTP/3 improves performance by leveraging QUIC, offering faster connection establishment and better error recovery.
- It enhances user experience, especially for mobile and international audiences, leading to better SEO outcomes.
- Adopting HTTP/3 can lead to measurable improvements in load times, engagement, and conversions.
- Tools like Cloudflare and DebugBear provide valuable insights and simplify the implementation process.
- Staying ahead of the curve with HTTP/3 ensures your website remains competitive in an increasingly fast-paced digital world.
Meta Title: Understanding HTTP/3: How the Latest Protocol Boosts Faster Data Transfer
Meta Description: Discover how HTTP/3 improves web performance, enhances user experience, and boosts SEO rankings. Learn the benefits and steps to implement this cutting-edge protocol.
SEO Tags (5): HTTP/3, Web Performance, SEO Optimization, QUIC Protocol, Faster Data Transfer
Internal Link Suggestions: [Parameter #65: HTTP/3 Adoption], [Parameter #64: Mobile Responsiveness], [Parameter #63: Server Response Optimization]
External Source Suggestions: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/logs.html, https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ssl/what-happens-in-a-tls-handshake/, https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Quic